Chainlink, one of the prominent altcoins in the cryptocurrency markets, recently made a significant change. This move has fueled criticisms regarding the decentralized narrative of the crypto community. What was it that targeted the monopolistic cryptocurrency venture in the field of blockchain-based oracle solutions?
Chainlink News
The decentralized oracle network, Chainlink, has made an important change in its multisignature wallet. Multisignature wallets are designed to prevent any transaction without the signatures of multiple authorities. For example, in today’s financial world, companies allow managers to sign decisions according to their authority in the signature circular. In some cases, multiple authorities are required for certain decisions, and even the signatures of the entire board of directors are required for more important decisions.
Critical decisions in crypto companies are also implemented on smart contracts. These decisions are implemented using multisignature wallets, which are authorized to execute them. For example, recently, the majority of the PEPE Coin management took action to exploit the treasury. In these wallets, when 4 out of 5 or 3 out of 5 keys provide approval, a transaction can be carried out. Generally, a majority is required for high-level security.
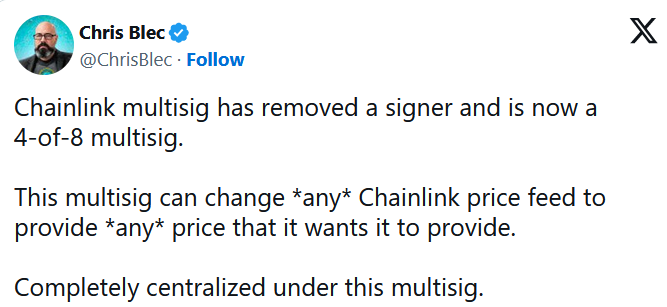
Crypto researcher Chris Blec recently criticized Chainlink for quietly reducing the required number of signatures in its multisignature wallet from 4 out of 9 to 4 out of 8. The 4-of-8 multisignature requirement is a security measure that requires four out of eight signatures to authorize a transaction. The new move deserves the criticism according to the previous rules.
Chainlink (LINK) Current Situation
The crypto community has been criticizing the Chainlink team for this move, which seems vulnerable to criticism at first glance. Just like Blec did. However, today, a Chainlink spokesperson stated in a statement that the update is part of a standard signer rotation process to ensure the reliable operation of Chainlink services.
“As part of the periodic signer rotation process, the multisignature Gnosis Safes used to ensure the reliable operation of Chainlink services have been updated. The rotation of signers has been completed, and the Safes maintain their standard threshold configuration (4 out of 9).”
Most DeFi platforms use the Chainlink infrastructure and obtain services for price feeds from it. Therefore, if the four authorized signers deviate from their path, we may see the sudden halt of most DeFi protocols. According to Blec, the centralization risk inherent in Chainlink jeopardizes the future of several fundamental DeFi projects relying on Chainlink’s oracles for price data, including Aave and MakerDAO.