Tokenization, or in other words, the process of transforming sensitive data into unique tokens without any meaningful value, is one of the data security and privacy methods used to protect sensitive information against unauthorized access. While tokenization plays a vital role in areas such as blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies, the term “token” carries a slightly different meaning in this context.
What is Tokenization?
So, what exactly is tokenization? It works by replacing sensitive data with randomly generated tokens. These tokens are usually alphanumeric strings and are stored in a secure database or token pool. The match related to the original data is preserved in the tokenization system. When the original data is needed, the token is used to retrieve information from the secure database.
Tokenization offers many advantages in data security. First, since tokens are meaningless, they reduce the risk of sensitive information being exposed, and it becomes impossible to reconstruct the original data using tokens. Even if tokenized data is seized or stolen, it becomes useless to an unauthorized person. Secondly, tokenization helps organizations comply with data protection regulations in areas such as the payment card industry by removing sensitive data from their systems and reducing the scope of compliance evaluations.
Where is Tokenization Used?
But where is tokenization used? It is utilized in various industries and applications where data security is important. One of the areas where tokenization is commonly used is the payment industry. Vendors use credit card tokenization to protect bank or credit card information of the customer during the payment process. Instead of actual credit card numbers, tokens are used to facilitate payment transactions and reduce the risk by preventing data theft and unauthorized access to sensitive financial information. Also, tokenization is used in the health sector, helping to protect sensitive data such as patient records and personal identification information. By tokenizing health data, organizations can store and transmit patient information securely and comply with privacy regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This ensures the protection and confidentiality of patient data, even in the event of a security breach.
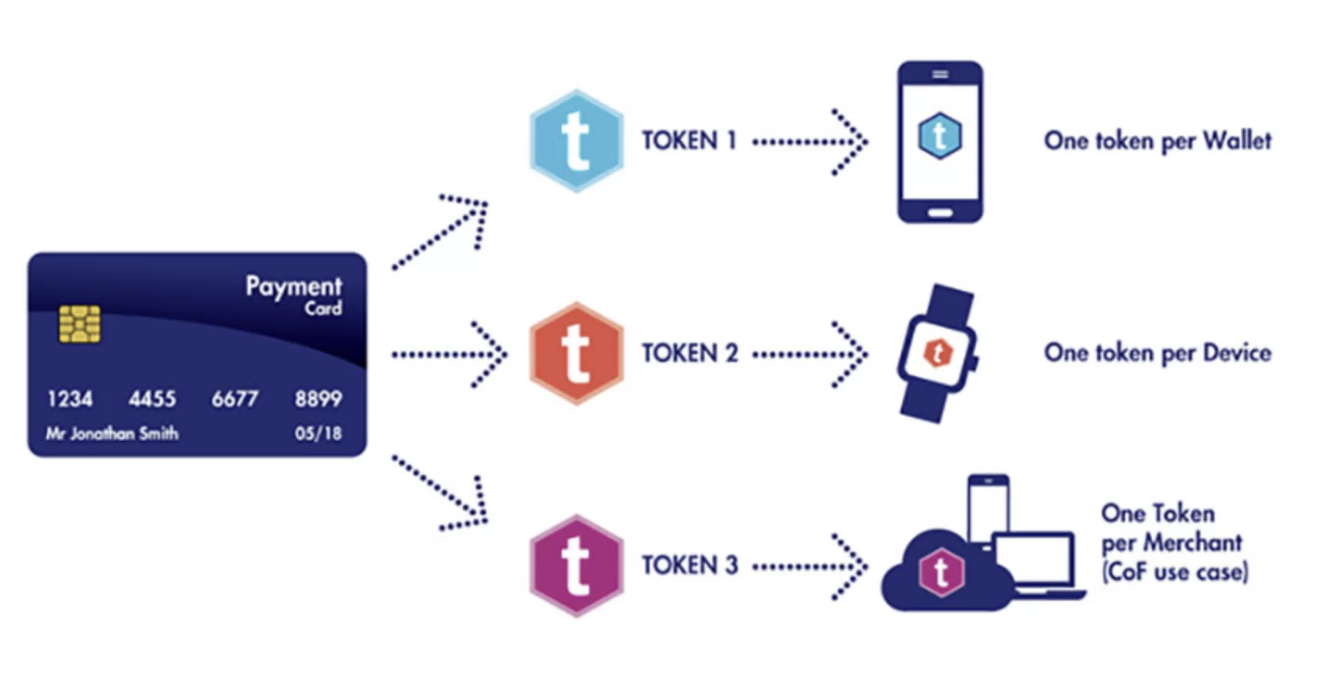
Tokenization is used in identity and access management systems, ensuring the security of user identity information. By using tokens representing users instead of usernames and passwords, the authentication process is strengthened, and the protection of user information is ensured. This helps prevent unauthorized access and identity theft.
Tokenization also plays a crucial role in blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. However, the term “token” has a slightly different meaning here. Here, the terms “coin” and “token” represent different things. A “coin” represents a cryptocurrency that operates independently on its own blockchain, while a “token” represents assets created on any existing blockchain networks. Tokens are usually found on platforms like Ethereum, where smart contracts operate and are used for various applications.
Coin and Token
Coins and tokens are terms commonly used in the Blockchain and cryptocurrency industry, each holding different meanings. A coin usually represents an independent cryptocurrency existing on its own blockchain. Coins are the fundamental units of cryptocurrencies and typically have their own blockchains. For instance, coins like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) transact on their blockchain networks and can be independently transferred, stored, and utilized. Coins often serve as a currency within an ecosystem, carrying direct value.
In contrast, a token represents cryptocurrency created and operated on an existing blockchain by smart contracts. Tokens are usually generated on another blockchain and transact using the features offered by this blockchain. For example, tokens created on the Ethereum blockchain can be used on a platform where smart contracts operate and various applications are used. Tokens generally represent value within a project’s economic system and provide specific utility within the project. Cryptocurrencies like Pepe (PEPE) and Shiba Inu (SHIB) are tokens because they operate on the Ethereum blockchain.
Key differences between a coin and a token include:
- Independence: While coins function as independent entities with their blockchain, tokens represent assets created and operating on an existing blockchain.
- Blockchain Network: Coins typically transact on their blockchain networks, while tokens operate on another blockchain, utilizing its features.
- Functionality: Coins are primarily used as a medium of payment, whereas tokens represent a specific value within a project’s economic system and offer access to the project’s services or features.
- Creation Process: Coins are typically created through mining or another consensus mechanism, while tokens are usually created on a blockchain network where smart contracts operate and have a certain logical structure.
In summary, while coins represent an independent cryptocurrency, tokens represent assets created on an existing blockchain platform and represent a specific value within the project’s economic system.
Types of Tokens
Tokens can be of different types. “Utility tokens” are tokens used for a specific service or product within a project. For instance, an in-game currency based on a blockchain can be considered a utility token. “Security tokens” represent financial assets, similar to stocks or bonds, serving as the digital counterparts of traditional financial instruments. “Non-fungible tokens” (NFTs) represent unique digital assets that cannot be interchanged with each other. For example, digital artworks or collectibles can be represented as NFTs.

 Türkçe
Türkçe Español
Español