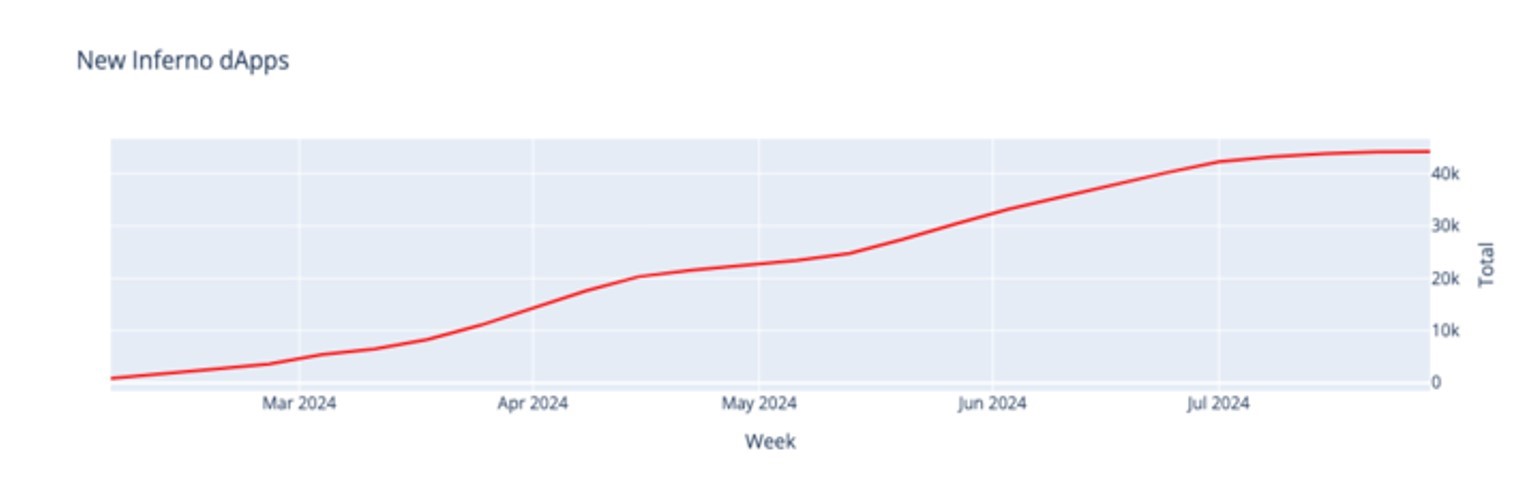
As the crypto market conditions improve, the number of decentralized applications (DApps) using the notorious Inferno Drainer tool has tripled as scammers increase their efforts to steal investors’ assets. According to data sent by Web3 security firm Blockaid, the number of DApps using Inferno Drainer rose to 40,000 by the end of July 2024.
Important Warning from a Renowned Expert
Blockaid’s research and development leader Oz Tamir said the number of new malicious DApps using the tool has tripled:
“At the beginning of the year, we saw about 800 new malicious DApps per week. Now this number has tripled to 2,400 per week.”
These platforms are phishing tools specifically designed for crypto. These applications allow phishing scammers to trick users into signing token approvals, giving them access to wallets. As a result, it provides these malicious actors with a way to steal funds. Inferno Drainer helped steal $70 million before claiming to shut down in 2023. However, the scam service tool has re-emerged and has become increasingly active this year.
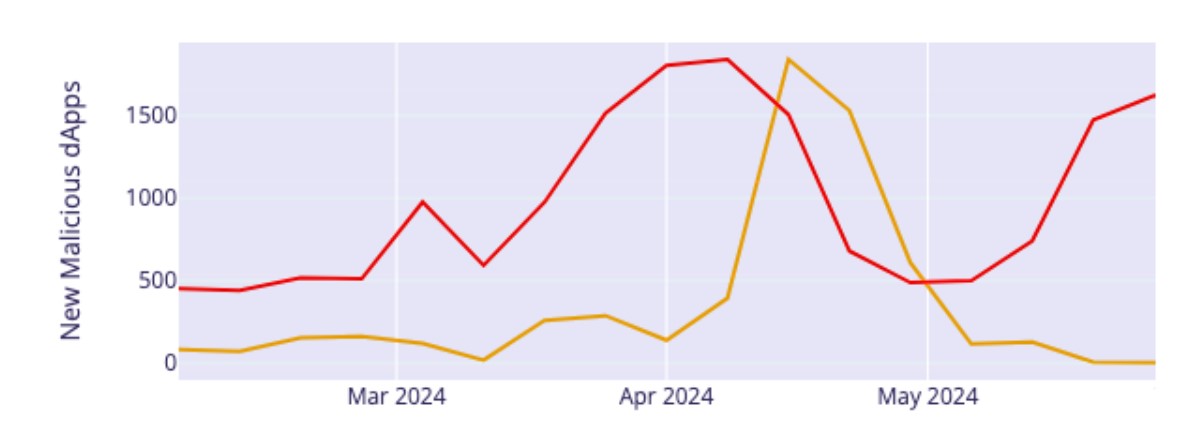
Inferno tool may seem sophisticated, but Tamir believes it is nothing special and says it is just a tool available to scammers right now. The security researcher explained that scammers often change tools based on what is currently available:
“To be honest, we don’t think Inferno has a specific capability that makes it superior to others. Scammers usually choose their methods based on what is available and the commission taken by the drainer.”
Details on the Subject
Tamir believes the increase is associated with growing fraud attempts among different threat actors. The Blockaid research leader revealed that at the beginning of 2024, they saw an average of 180,000 malicious scan results per week. Tamir also believes this trend is related to the current bull market conditions the crypto space has experienced in recent months. The Web3 researcher explained this topic as follows:
“As more users and money enter the ecosystem, attackers are increasingly motivated to invest in new and original attacks.”
The researcher added that attackers are also taking advantage of new chains being deployed. Tamir believes these new ecosystems have fewer security measures, and attackers see them as an opportunity to make quick money.
 Türkçe
Türkçe Español
Español