In the last few years, institutional interest in Bitcoin (BTC) has peaked. The increase in the number and capital of public Bitcoin mining companies has become much more attractive to giant corporations like BlackRock.
However, the returns these companies have received for their investments so far carry significant challenges that need to be overcome going forward. In particular, the latest data provided by CompaniesMarketCap shows a total loss of $2.75 billion for the sector among 17 companies.
The Current State of Bitcoin Miners
Bit Digital (NASDAQ: BTBT) is known as the “most profitable” public Bitcoin mining company. Following the downturn in the cryptocurrency market since the end of 2021, especially since the fourth quarter of 2022, it has suffered a loss of $28.39 million, placing it at the top of the list. Nevertheless, compared to even worse outcomes in the market, this might be considered insignificant. It is useful to note that BTBT’s market value is $300 million.
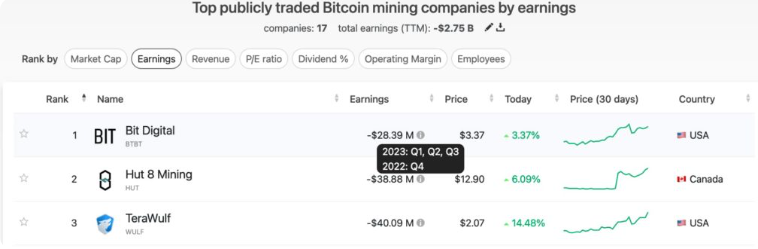
Meanwhile, losses are also mounting for the top three public Bitcoin mining companies. The top three companies are Marathon Digital Holdings (NASDAQ: MARA), Riot Blockchain (NASDAQ: RIOT), and Hut 8 Mining (NASDAQ: HUT), with market values of $4.85 billion, $3.52 billion, and $2.86 billion, respectively.
Speaking of their losses, MARA reported a loss of $380 million. RIOT experienced a loss of $300 million, slightly less than MARA, while HUT reported a relatively more positive picture with a loss of $38.88 million.
The Challenges of Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is an extremely competitive environment. Generally, in processes every 10 minutes, a block is mined by a single organization that receives rewards through block subsidies or fees. On the other hand, as participation in competition increases, costs also rise.
Moreover, after the mining process is completed and the reward is received, these organizations need to sell the BTC they have earned to cover their expenses. Essentially, this situation ties the profitability of Bitcoin mining companies largely to the price of Bitcoin, while also leading to a dependency on higher centralization.
Furthermore, higher centralization can cause disruptions in the secure environment of Bitcoin and alter its perceived value.
 Türkçe
Türkçe Español
Español