As the rise in the cryptocurrency market continues, significant developments in the blockchain field keep making headlines. Accordingly, StarkWare announced the introduction of ZKThreads, a new scaling framework designed to prevent fund traps and enhance the scalability of decentralized applications (DApps). Louis Guthmann, the head of strategy, made notable statements on the subject.
StarkWare Team Takes Significant Step
StarkWare product/market strategy head Louis Guthmann discussed the impact of ZKThreads, stating that StarkWare’s layer scaling technology could prevent a disaster like FTX and made the following remarks:
“What ZKThreads adds is the ability to ensure users can continue transacting even in a disruption scenario. For example, if a centralized exchange goes bankrupt, users can automatically transact through the base layer. This will keep markets efficient, especially on the futures side.”
Developed in collaboration with Cartridge, ZKThreads aims to overcome fragmentation issues by creating a standardized environment for easily verifiable applications. This is based on StarkWare’s vision of fractal scaling, introduced in 2021, as an alternative to modern ZK systems that typically operate separately, leading to fragmented liquidity, resources, and reduced application connectivity.
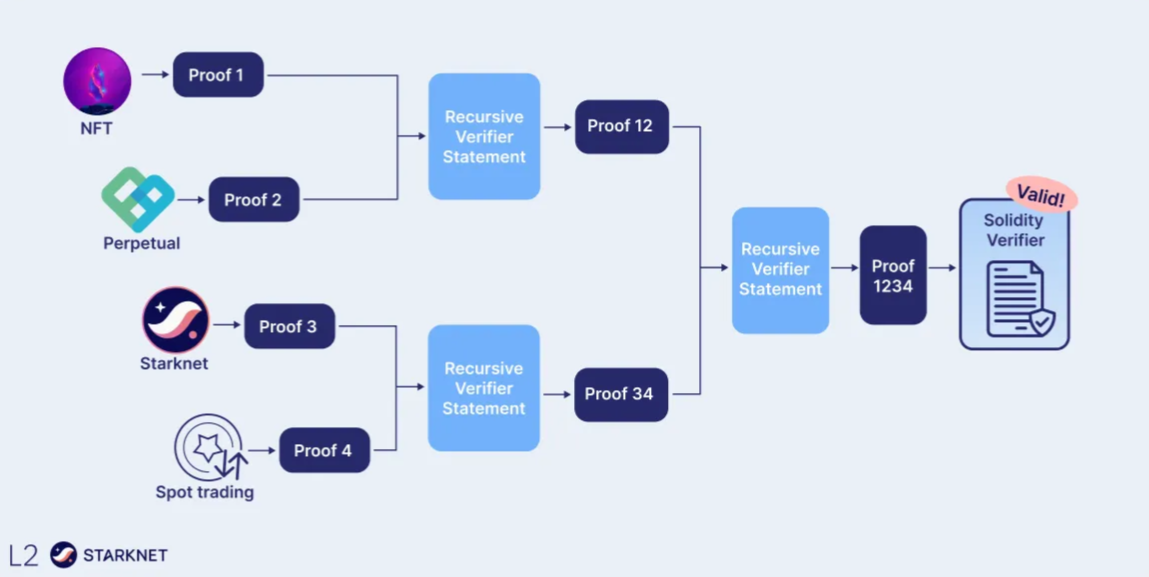
What’s Happening in the ZK Field?
ZKThreads project initiator Guthmann explained that there are broad implications for how we create DApps and commented:
“Since the blockchain field primarily focuses on layer-based scaling, this opens the doors to an entirely new world. This is very important, but ZKThreads highlights the potential of horizontal scaling as a complementary approach.”
StarkWare’s Layer-2 solution Starknet enables this horizontal scaling through execution sharing enhanced by zero knowledge (ZK) proofs. This process involves breaking down tasks into smaller parts while ensuring the confidential details of each executed task remain accurate, secure, and private. Guthman added:
“ZKThreads rethinks joint processing by synchronizing with the main chain, avoiding the typical isolation found in traditional models. This increases security and trust, creating a seamless fabric of interoperable applications.”










