The security of cryptocurrency wallets is crucial for investors since these wallets are stored on devices. If a hacker gains access to a computer or phone, the cryptocurrency wallet can be easily emptied. Furthermore, attackers target investors with applications that antivirus software often does not detect, appearing legitimate even after passing Apple’s approval.
Apple Security Vulnerability
Researchers from Jamf Threat Labs, who monitor Apple systems, discovered new malware that bypasses security controls. The source of these malicious programs is believed to be North Korea, which has a history of training hackers for public attacks to finance its nuclear program.
In their analysis, the team described this malware as a first-of-its-kind attack. Crypto Traders Are Rushing to This App – Here’s Why You Should Too
“Jamf Threat Labs has found malware samples believed to be linked to the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), which evade detection through obfuscation techniques. They are investigating how this malicious code operates, particularly targeting macOS devices and users with potential new methods.”
The malware manifests itself in three forms: a Go variant, a Python variant created with Py2App, and an application developed with Flutter.
Investors Must Exercise Caution
Attackers on GitHub use malicious versions of applications as traps for victims. VirusTotal usually analyzes uploaded files against multiple antivirus databases, allowing users to operate safely with a “zero malware detection” warning.
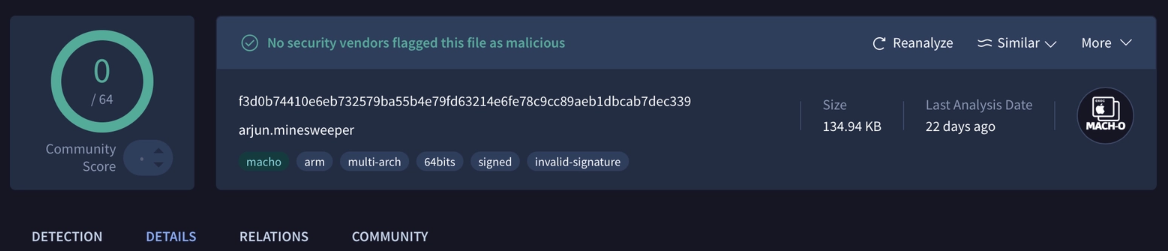
However, there is a significant concern. There are techniques that complicate code structures, making it difficult to identify malicious codes. While these disguised malware samples can be detected through specialized examination, they may appear clean for a week or ten days before antivirus companies initiate their review processes.
When targeted specifically and scanned less frequently, this malware can maintain a “privacy shield” longer. This process, known as FUD masking, means that even premium antivirus software might fail to detect the malware in use. Additionally, these applications may falsely display that they are signed by Apple, further gaining the victims’ trust.
Therefore, it is advisable to use hardware wallets whenever possible and frequently monitor data exfiltration alongside antivirus software to check for internal leaks. Using advanced applications like Wireshark can help examine data packets for unusual activity.
The best security measure is to avoid installing unnecessary applications on devices and understanding that using programs beyond those from trusted companies always carries risk.
In their final notes, the security team highlighted crucial points regarding the links of malware to terms like Stablecoins, DeFi, CeFi, and Multisig risks in cryptocurrency.
“North Korean hackers have a notorious reputation for creativity. In October, they exploited a security vulnerability in Chrome to steal cryptocurrency wallet credentials, and claims arose about their involvement in developing the Liquid Staking Module for the Cosmos network. According to the United Nations, these hackers are highly organized and reportedly acquire hundreds of thousands of dollars worth of cryptocurrency monthly, accumulating around 3 billion dollars over the last six years.”

 Türkçe
Türkçe Español
Español