According to a report prepared by the United Kingdom’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC), the field of artificial intelligence could significantly increase cyber threats, including ransomware attacks, in the next two years. The NCSC report summarized how artificial intelligence could be leveraged to strengthen cybersecurity through detection and advanced design to balance its impact on cyber threats.
Artificial Intelligence and the Field of Cybersecurity
The NCSC report recommended further research to measure how developments in artificial intelligence in the cybersecurity field could reduce the impact of threats. Ransomware attacks are known as a cyberattack method where malicious software is used to encrypt the victim’s files or entire system. Attackers then typically demand a ransom in cryptocurrency to provide the decryption key or tools to restore access to the data.
The impact of the artificial intelligence field on cyber threats is expected to shift in favor of advanced state actors with more access to advanced AI-driven cyber operations. The report highlights social engineering as a critical area where artificial intelligence’s capabilities will significantly improve, making phishing attacks more convincing and harder to detect.
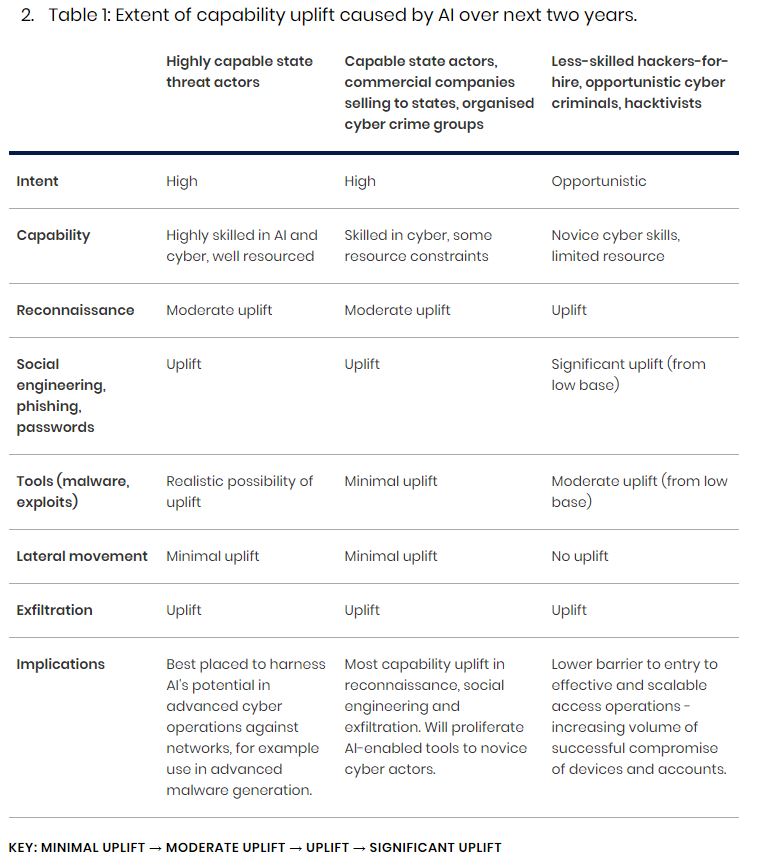
The NCSC report states that artificial intelligence will primarily enhance threat actors’ capabilities in the area of social engineering. Generative AI can create convincing interactions free from translation and grammatical errors common in identity theft, and this trend is expected to grow as models develop and gain popularity over the next two years. Supporting this statement, NCSC’s Director of Threats James Babbage said:
“Artificial intelligence services will reduce entry barriers, increasing the number of cybercriminals and enhancing the scale, speed, and effectiveness of their current attack methods.”
What Are the Notable Details in the Report?
The NCSC assessment points to challenges in cyber resilience due to artificial intelligence models such as generative AI and large language models. These models make it difficult to verify the legitimacy of emails and password reset requests. The reduced time between the emergence of threats and security updates makes it difficult for network administrators to quickly close security vulnerabilities.
As utilizing advanced artificial intelligence in cyber operations requires expertise, resources, and access to quality data, government agencies are best positioned to benefit from the potential of artificial intelligence. According to the report, other government institutions and corporate companies will see moderate capability gains within the next 18 months.
While NCSC acknowledges the importance of skills, tools, time, and money for the use of advanced artificial intelligence in cyber operations, the report indicates that these factors will become less important as AI models become more widespread. It is predicted that the accessibility of AI-featured cyber tools will increase as skilled groups profit from AI-featured cyber tools and offer advanced capabilities to anyone willing to pay.
 Türkçe
Türkçe Español
Español