The Akira ransomware group has breached the security of over 250 organizations, and according to warnings from leading global cybersecurity agencies, it has generated approximately $42 million in ransomware revenue. Investigations conducted by the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) have revealed that since March 2023, the Akira ransomware has targeted businesses and critical infrastructure organizations in North America, Europe, and Australia.
Cybersecurity Threat of Akira
Initially targeting Windows systems, the FBI recently found that Akira has also developed software targeting Linux systems. The FBI, along with the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), Europol’s European Cybercrime Centre (EC3), and the Dutch National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC-NL), has issued a joint cybersecurity advisory (CSA) to prevent the threat to the masses.
According to the advisory, Akira initially gains access through pre-installed virtual private networks (VPNs) lacking multi-factor authentication (MFA). The ransomware then continues to extract credentials and other sensitive information before locking the system and displaying a ransom note:
“Akira threat actors do not leave an initial ransom demand or payment instructions on the compromised networks and do not transmit this information until they contact the victim.”
The ransomware group demands payment in Bitcoin from victim organizations to restore access. This type of malware often disables security software after initial access to avoid detection.

Noteworthy Comments on the Issue
Some of the threat mitigation techniques recommended in the advisory document include implementing a recovery plan and multi-factor authentication, filtering network traffic, disabling unused ports and bridges, and system-wide encryption. The agency stated the following:
“The FBI, CISA, EC3, and NCSC-NL recommend that you continuously test your security program on a large scale and in a production environment to best counter the MITRE ATT&CK techniques identified in this advisory document.”
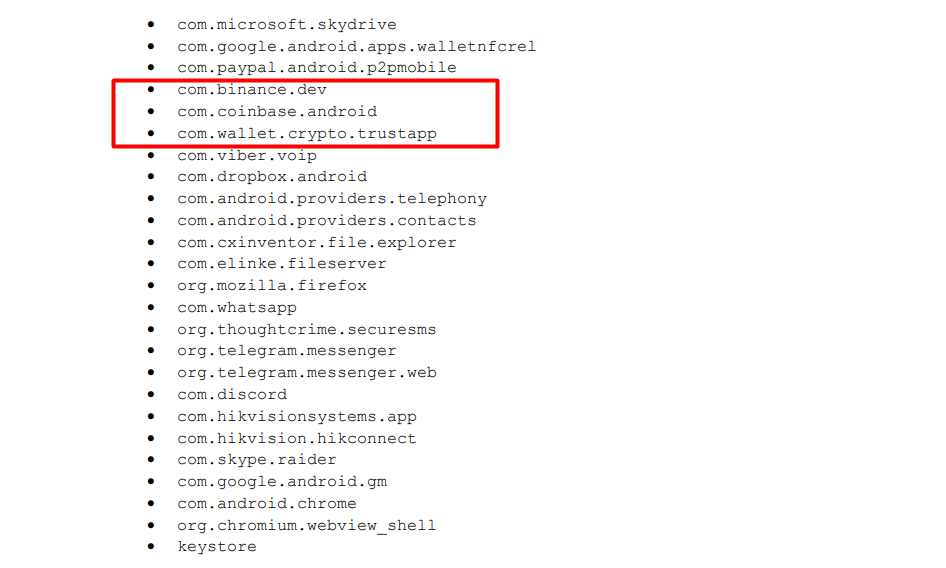
The FBI, CISA, NCSC, and the National Security Agency (NSA) had previously issued warnings about malware targeting cryptocurrency wallets and exchanges. The report indicated that some of the data extracted by the malware included directories of the Binance and Coinbase exchange applications and the Trust Wallet application. According to the report, every file type listed in these directories is being extracted.
 Türkçe
Türkçe Español
Español