JPMorgan analysts reported that the recent increase in Ethereum (ETH) staking has led to increased centralization and decreased staking returns. The analysts pointed out that a significant majority of Ethereum staking activity is controlled by Lido.
Ethereum Network Becomes More Centralized as Stake Returns Decrease
In the latest investor note by JPMorgan analysts led by Nikolaos Panigirtzoglou, it was emphasized that the increase in ETH staking since The Merge and The Shanghai updates has come with some costs, including the centralization of the Ethereum network and a decrease in overall staking returns.
The Merge update, which took place in September 2022, allowed Ethereum to transition from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake, enabling ETH staking. The Shanghai update in April allowed validators to unlock their staked ETH and reinvest, leading to an increase in staking activity.
Lido and Centralization Concerns
Liquidity staking providers like Lido have been the biggest contributors to the growth of staking in Ethereum. JPMorgan analysts stated, “The top 5 liquidity staking providers control over 50% of stake transactions in the Ethereum network, with Lido alone accounting for almost a third.” Despite being decentralized liquidity staking platforms, platforms like Lido contribute to a high degree of centralization.
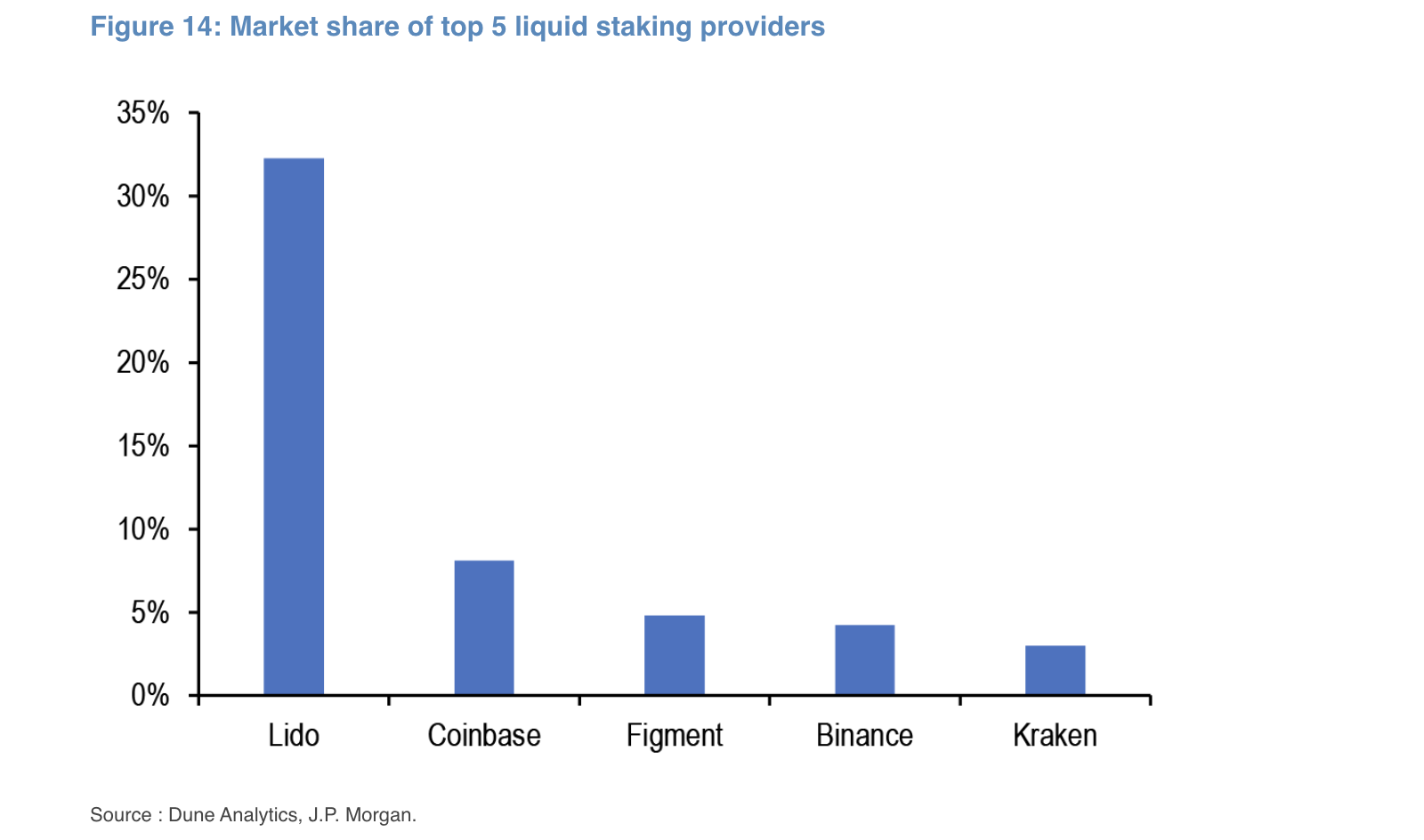
The analysts added, “It goes without saying that centralization poses risks for the Ethereum network, as a high number of liquidity providers or node operators can act as a single point of failure, become targets of attacks, or collaborate to create an oligopolistic market that supports their own interests at the expense of the community, such as censoring specific transactions or prioritizing their own transactions.”
In addition to centralization concerns, another concern arising from the growth of liquidity staking is the practice of using liquidity tokens as collateral in multiple DeFi protocols simultaneously. The analysts noted that this practice could lead to gradual liquidations in the event of a sudden drop in the value of a staked asset or a malicious attack or protocol failure.
 Türkçe
Türkçe Español
Español