In recent months, malware designed for cryptocurrency mining and theft has affected thousands of devices. However, the amount of cryptocurrency seized by cybercriminals remains around six thousand dollars.
Cybersecurity Threats Targeting Turkey
According to a statement from cybersecurity company Doctor Web on October 8, the malware spreads by disguising itself as legitimate software like office programs, game cheats, and online trading bots. The software has targeted over 28,000 users across several countries, including Turkey, Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, and Kyrgyzstan.
Malware Techniques for Crypto Theft
Infected devices have their processor resources secretly utilized for cryptocurrency mining. Additionally, the malware features a function called “Clipper,” which monitors copied cryptocurrency wallet addresses and replaces them with addresses controlled by attackers. This method has allowed the software to steal only a limited amount of cryptocurrency.
Doctor Web reported that the value of the stolen cryptocurrency is approximately six thousand dollars. However, the profits gained by the malware creators from mining activities remain unknown.
The malware employs various techniques to evade detection. It avoids antivirus scans using password-protected archives, disguises malicious files as legitimate system components, and executes harmful scripts through legitimate software.
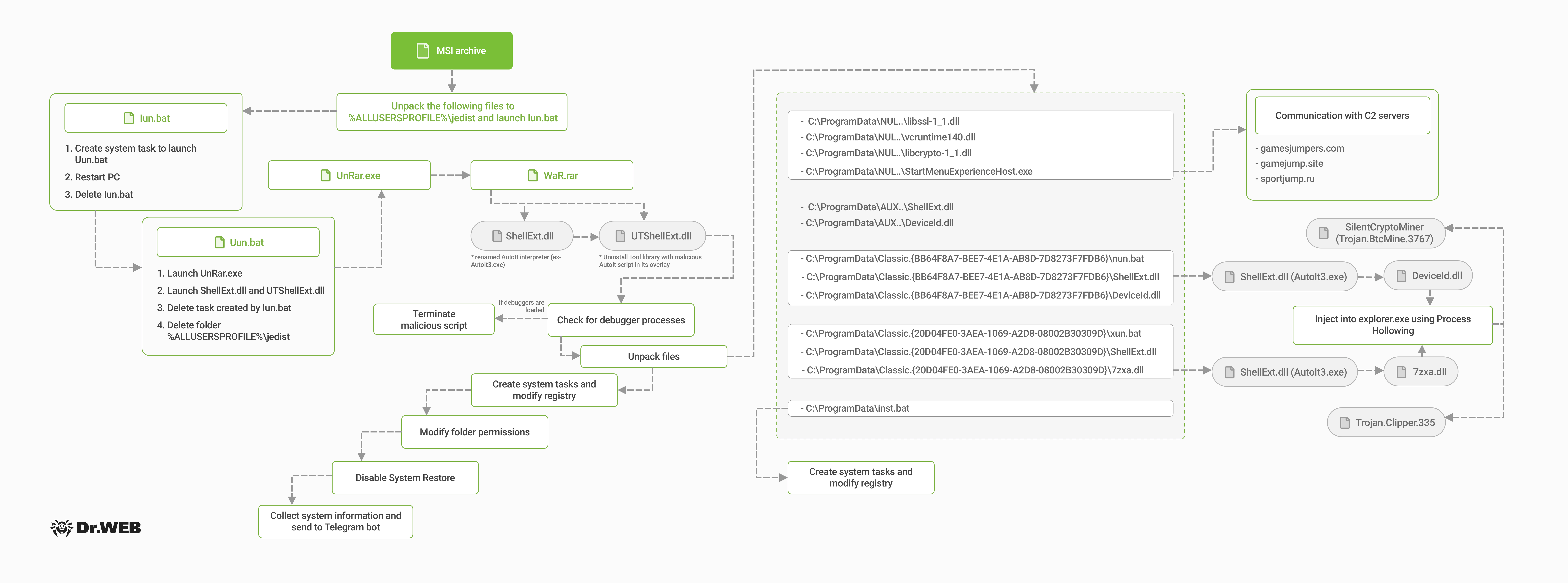
In September, the cryptocurrency exchange Binance warned about this malware named Clipper, noting an increase in its activity that led to significant financial losses for users. Doctor Web pointed out that the spread of the malware is facilitated by malicious links found on fake GitHub pages and YouTube video descriptions.
The cybersecurity firm urged users to download software solely from official sources, as many have risked their devices by installing pirated software. Malware that alters cryptocurrency wallet addresses has existed for years, becoming more prevalent after the cryptocurrency bull market in 2017. Such malware is increasingly complex, often combining clipboard theft functions with other malicious actions.
In September, the threat intelligence company Facct reported that scammers and malicious actors are utilizing automated email responses to spread cryptocurrency mining malware.
 Türkçe
Türkçe Español
Español