Also known as a stop-loss order, a stop order is a type of order used on a cryptocurrency exchange designed to limit potential losses or protect profits in a specific trade. It serves as an essential risk management tool for investors, initiating an automatic market order when a cryptocurrency’s price reaches a certain trigger price known as the stop price. In this article, we’ll delve into what a stop order is, how it works, and other related topics in cryptocurrency exchanges.
Stop Order: What Is It?
A stop order, frequently used in financial markets and available in crypto exchanges, is a stop-loss order. It’s a type of order given by investors to automatically execute a transaction when a cryptocurrency’s price reaches a specific stop price. In crypto exchanges, a stop order is generally used to limit potential losses or protect profits in cryptocurrency trading.
There are two types of stop orders: Sell stop order and buy stop order. A sell stop order is a sell stop order placed below the current market price of a cryptocurrency. It’s generally used to limit losses in a long position or initiate a short position. The sell stop order is triggered, and the cryptocurrency is sold at the best available price when the market price falls to or below the stop price. Conversely, a buy stop order is a purchase stop order placed above the current market price of a cryptocurrency. It’s used to enter a long position or close a short position. If the market price rises to or above the stop price, the buy stop order is triggered, and the asset is purchased at the best available price.
Stop orders are fundamental risk management tools for investors, as they allow for automatic implementation based on predetermined price levels. They help investors limit potential losses by selling an asset when it reaches a certain price level, thereby avoiding exposure to further downside risk. A stop order can also be used to protect profits by selling a cryptocurrency when it reaches the desired price level.
It’s crucial to underline that the execution of a stop order at the specified stop price is not guaranteed. In financial markets like the cryptocurrency market where there are sharp price movements or during periods of high volatility, a stop order can deviate from the stop price, resulting in the execution of the transaction with a slight deviation. Investors should consider certain risks such as market conditions, liquidity, and volatility when using a stop order.
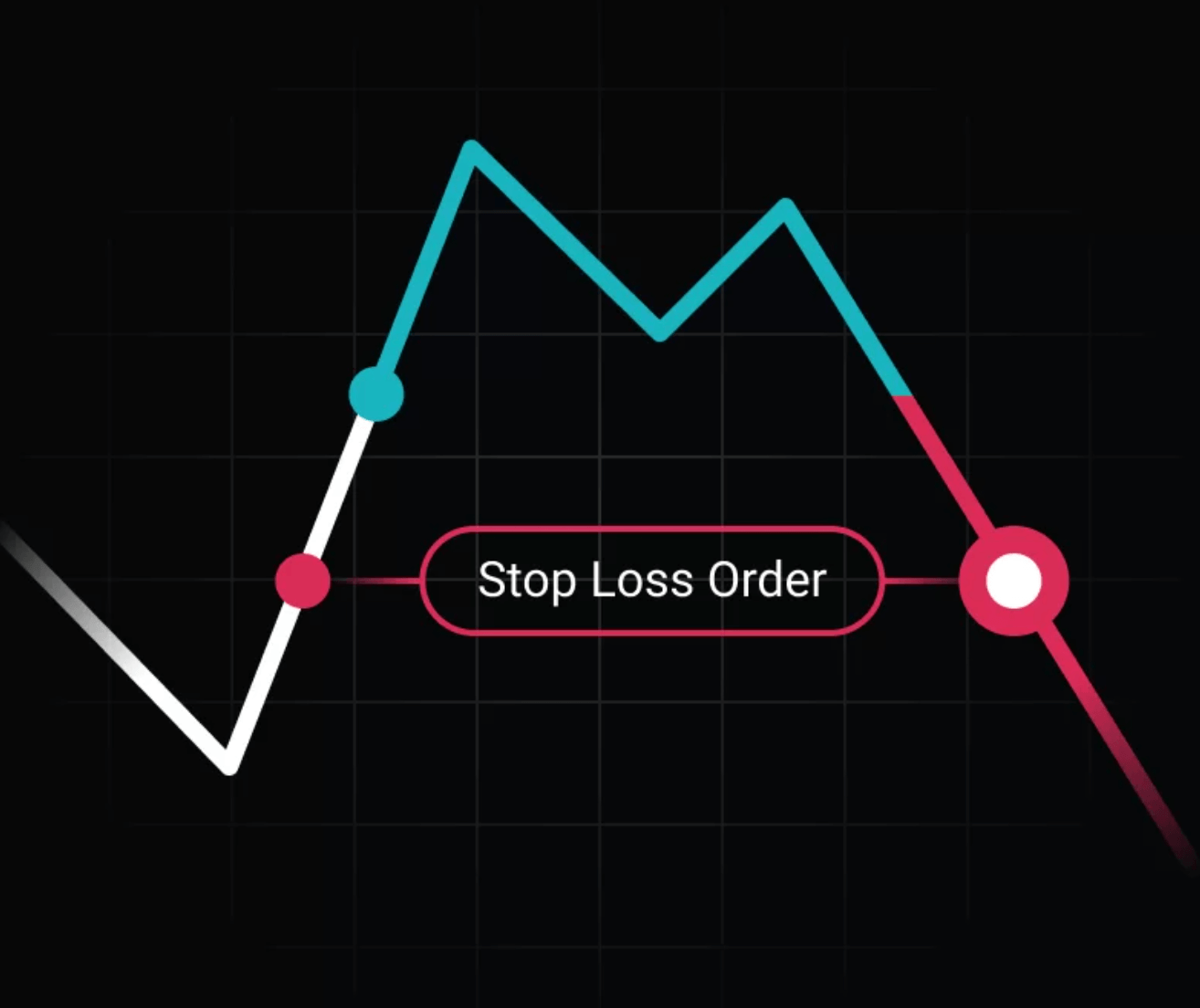
A stop order, often employed in financial markets and made available on crypto exchanges, is designed to automatically execute a transaction when a certain stop price is reached. This order type is often used by investors to limit potential losses or protect profits in cryptocurrency trading.
The Execution of Stop Orders
To understand how a stop order works, we need to explore the setting of the stop price, the activation of the stop order, and the execution of the market order sequentially.
An investor or trader specifies the stop price, the price level at which they want the order to be triggered, when placing a stop order. For example, if an investor has purchased Bitcoin (BTC) at 30,000 dollars and wants to limit potential losses, they can place a stop order at 29,000 dollars. When the price of the major cryptocurrency reaches or drops below the set stop price, the stop order is triggered and converted into a market order. A market order is executed immediately at the current market price, meaning the actual execution price may differ from the stop price. Once activated, the stop order acts like a regular market order, buying or selling the cryptocurrency at the most suitable price in the market.
The execution price can be somewhat above or below the stop price, particularly during periods of high volatility or low liquidity.
Using a stop order provides automatic risk management and helps prevent emotions from influencing trading decisions. By setting a stop price, investors can predefine acceptable maximum losses or target profit levels and manage their buying and selling operations more effectively.
However, the stop order is not flawless and does not offer absolute protection. In extremely volatile market conditions, such as sudden market crashes or situations with low liquidity, there could be delays in the operation of stop orders, or they might execute at significantly different prices than expected. Therefore, investors should always consider market conditions, liquidity, and potential risks associated with each crypto exchange before solely relying on stop orders for risk management.
 Türkçe
Türkçe Español
Español